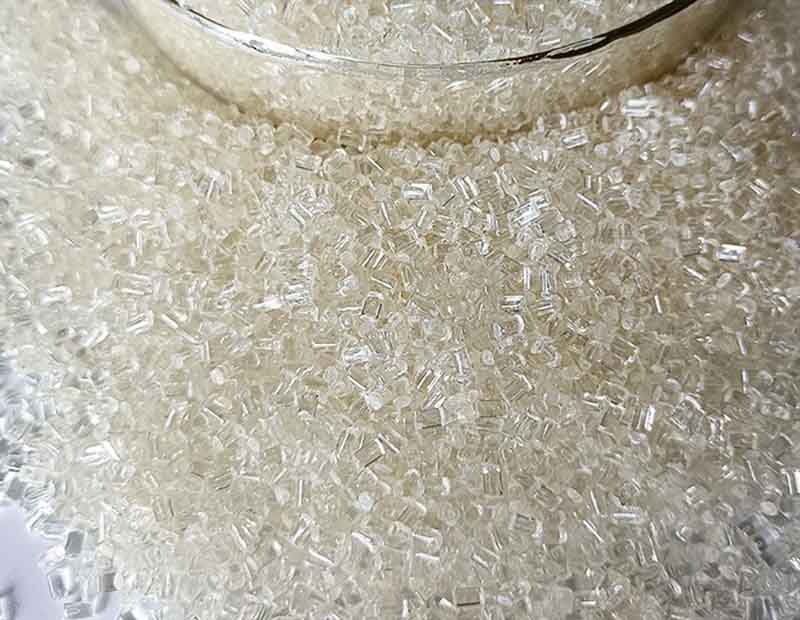
Polysulfone (PSU) is widely recognized as a High-performance thermoplastic with excellent thermal stability, mechanical strength, and chemical resistance. Used extensively in industries such as medical, automotive, aerospace, and water treatment, PSU delivers long-lasting reliability. However, as sustainability becomes a top priority in materials science, industries are now exploring how Polysulfone Materials can be more effectively recycled and integrated into eco-conscious manufacturing models.

1. Why Sustainability Matters in High-Performance Plastics
With rising environmental concerns and tightening regulations around plastic waste, industries are under pressure to reduce their carbon footprint. While commodity plastics like PET and PE have well-established recycling streams, engineering plastics such as PSU have historically been more difficult to recycle due to their specialized performance characteristics and processing requirements.
Yet, due to its long service life and potential for reuse, PSU presents unique opportunities for sustainability through responsible recycling and manufacturing practices.
2. Recycling Methods for Polysulfone
a. Mechanical Recycling
Polysulfone waste, such as offcuts or rejected molded parts, can be mechanically shredded and reprocessed under controlled conditions. While PSU is a thermoplastic and can be re-melted, repeated recycling may slightly reduce its thermal and mechanical properties. Additives or blending with virgin resin are often used to maintain quality in second-life applications.
b. Chemical Recycling
Although still in the research and pilot stages, chemical recycling of PSU involves depolymerization, breaking the material down to its monomer units for purification and reuse. This method shows promise for achieving a closed-loop system but remains cost-intensive and technologically challenging.
c. Energy Recovery
When reuse or recycling is not feasible, PSU waste can be used in energy recovery processes through incineration in energy-generating plants. This ensures waste is not landfilled, though it is considered a last resort from an environmental perspective.
3. Eco-Friendly Manufacturing Practices
Lower VOC Emissions
Polysulfone resin production has improved with cleaner processes, leading to lower emissions of volatile organic compounds (VOCs), contributing to safer work environments and reduced environmental impact.
Use of Recycled Feedstocks
Some manufacturers are beginning to incorporate recycled raw materials or secondary polymers during resin synthesis. While this is still limited for PSU compared to commodity plastics, the trend is growing.
Energy Efficiency in Production
Modern processing equipment for PSU molding or extrusion is designed for higher energy efficiency, with lower scrap rates and improved material utilization.
4. Sustainable Applications of Polysulfone
Polysulfone’s long service life reduces the need for frequent replacement, which contributes to less waste over time. Typical sustainable applications include:
Reusable medical devices (e.g., surgical handles, sterilization trays)
Durable filtration components in water treatment and food processing
Lightweight, fuel-saving parts in automotive and aerospace industries
These uses underscore PSU's alignment with sustainability goals by offering high durability and extended use cycles.
5. Future Trends and Industry Commitments
The push toward a circular economy has prompted many resin producers to invest in advanced recycling technologies and greener production lines. As demand for eco-friendly materials rises, PSU suppliers are expected to increase transparency in lifecycle data, carbon footprints, and compliance with international environmental standards (e.g., REACH, RoHS, ISO 14001).
Collaborations between material scientists, recyclers, and end-users are also accelerating the development of recyclable PSU grades and biodegradable additives.
While recycling polysulfone resin remains more complex than conventional plastics, progress in mechanical recovery, sustainable manufacturing, and eco-oriented product design offers a promising path forward. As the materials industry continues to prioritize environmental responsibility, polysulfone will play an important role—not just as a high-performance thermoplastic, but also as a sustainable material solution for the future.