In today’s fast-paced industrial world, manufacturers are constantly searching for materials that combine strength, versatility, and cost-efficiency. Among the many options available, Engineering Plastic rod & sheet have emerged as some of the most valuable Semi-Finished Products for industrial manufacturing. Their unique properties not only rival traditional metals but also open new opportunities for innovation across a wide range of industries.
This article highlights the key benefits of using engineering plastic rods and sheets in industrial applications and explains why more manufacturers are making the shift toward these advanced materials.
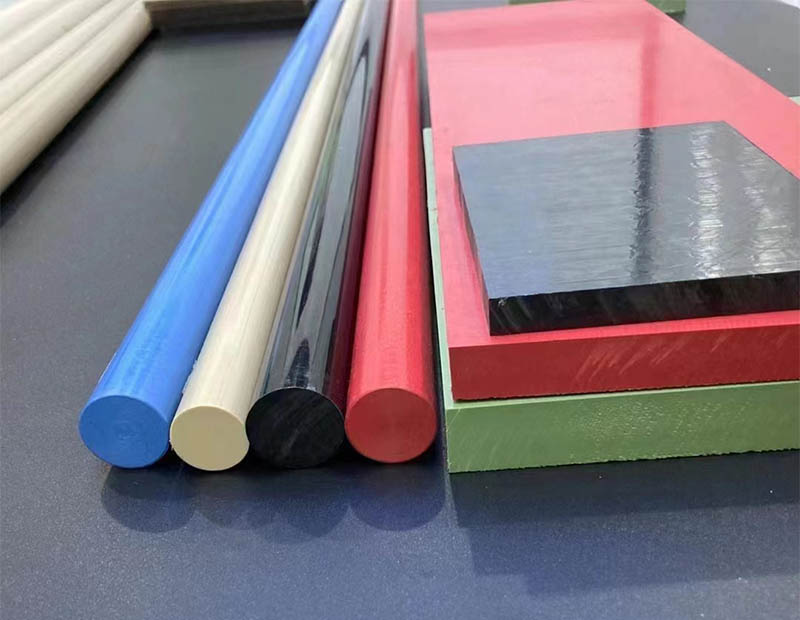

1. Lightweight Yet High Strength
One of the biggest advantages of engineering plastic rods and sheets is their ability to deliver high mechanical strength while being significantly lighter than metal. For industries such as automotive, aerospace, and machinery manufacturing, weight reduction plays a crucial role in improving performance and reducing energy consumption.
By replacing metal parts with engineering plastics, companies can design components that are easier to transport, install, and operate without sacrificing durability. This makes them an ideal choice for semi-finished products that will later be machined into gears, bearings, bushings, or housing components.
2. Excellent Chemical and Corrosion Resistance
Unlike metals, which often require coatings or treatments to resist corrosion, engineering plastics are inherently resistant to a wide variety of chemicals, oils, and solvents. This property makes engineering plastic sheet and rod materials highly suitable for environments exposed to aggressive substances, such as chemical processing plants, marine equipment, or laboratory devices.
In industrial manufacturing, this translates into longer product life cycles and reduced maintenance costs. Semi-finished products made from POM (polyacetal), PTFE (Teflon), or PVDF, for example, are highly sought after for chemical storage tanks, valves, and piping systems.
3. Superior Wear and Friction Performance
Engineering plastic rods and sheets are frequently used to manufacture components like bearings, sliders, and gears because of their low friction coefficient and self-lubricating properties. Unlike metals, they do not require constant lubrication, making them cleaner and easier to maintain.
For industries where machinery must operate continuously, such as packaging, textiles, or food processing, engineering plastics reduce downtime and extend service intervals. This efficiency has made semi-finished products in plastic form a preferred choice for manufacturers seeking long-term performance and reliability.
4. High Impact and Shock Absorption
Certain engineering plastics, such as nylon and polycarbonate, provide exceptional impact resistance. When used in industrial equipment, they act as shock absorbers, protecting delicate machinery from sudden forces.
This ability to withstand shocks and vibrations makes engineering plastic sheets and rods useful in automotive bumpers, protective covers, and machine guards. By using these semi-finished products, manufacturers can enhance workplace safety while ensuring consistent production performance.
5. Easy Machining and Customization
One of the reasons engineering plastic rods and sheets are widely adopted in industrial manufacturing is their versatility in machining. These materials can be easily cut, drilled, milled, and shaped into custom components with high precision.
Compared with metals, they require less energy during processing and do not damage cutting tools as quickly. This translates to cost savings and faster turnaround times. Many companies now source semi-finished products in plastic form so that they can be customized on-site or through CNC machining to match unique design requirements.
6. Thermal and Electrical Insulation
Another critical benefit is the excellent thermal and electrical insulation provided by many engineering plastics. This makes them indispensable in industries like electronics, power generation, and telecommunications.
Plastic sheets and rods such as epoxy laminates, phenolics, and PVC are used in switchgear panels, insulators, and electronic housings. These semi-finished products not only enhance equipment safety but also contribute to energy efficiency by minimizing heat loss and electrical leakage.
7. Cost-Effectiveness and Long-Term Value
While the initial cost of certain engineering plastics may be higher than metals, their longer service life, lower maintenance requirements, and ease of processing result in significant cost savings over time.
For industrial manufacturers, this means better ROI (return on investment) and improved production efficiency. Semi-finished products in plastic form allow businesses to balance quality with affordability, making them a smarter choice for competitive markets.
8. Wide Range of Material Options
The versatility of engineering plastics lies in the wide selection of available materials, each offering unique benefits. Common options include:
POM (Polyacetal): High strength, low friction, good dimensional stability.
PA (Nylon): Excellent wear resistance, shock absorption, toughness.
PC (Polycarbonate): High impact strength, transparency, heat resistance.
PTFE (Teflon): Outstanding chemical resistance, low friction.
PEEK: Exceptional thermal stability, strength, and chemical resistance.
This variety ensures that manufacturers can always find the right semi-finished products to meet their specific needs.
9. Environmental and Sustainability Benefits
Sustainability has become a core priority in modern manufacturing. Many engineering plastics are recyclable, and their lightweight nature reduces energy consumption during transportation and operation.
In addition, semi-finished products made from bio-based or eco-friendly plastics are gaining popularity, helping companies align with global sustainability goals while maintaining performance standards.
10. Versatile Applications Across Industries
Engineering plastic rods and sheets have become indispensable across industries such as:
Automotive & Aerospace: Gears, bearings, and lightweight structural parts.
Electronics: Insulators, housings, and switch components.
Medical & Food Industry: Hygienic, FDA-approved plastic components.
Chemical Industry: PiPES, tanks, and resistant linings.
Machinery & Equipment: Wear strips, rollers, and guards.
This broad applicability underscores their role as essential semi-finished products in modern industrial manufacturing.
Conclusion
The shift toward engineering plastic rods and sheets in industrial manufacturing is more than a trend—it is a reflection of their superior performance, versatility, and cost-effectiveness. As industries evolve, the demand for durable, lightweight, and customizable materials continues to rise.
By leveraging engineering plastic semi-finished products, manufacturers can optimize production processes, reduce costs, and deliver long-lasting solutions that meet the demands of today’s competitive markets.
In a world where efficiency and sustainability are paramount, engineering plastics stand out as the material of choice for the future of industrial manufacturing.